We have the technology to make it a reality
Think In 3D
A PREMIEUM 3D DESIGNING & PRINTING AGENCY IN KOLKATALEARN MORE

Architects and other AEC professionals are increasingly using 3D printers to produce beautiful, physical, and highly-detailed architectural models. The experts can now showcase their ideas and impress their clients with tangible models that take into account precise building or construction site information. They are saving time and money as well as winning more business by utilizing 3D printing to create intricate and durable designs straight from CAD data

The aerospace industry includes a range of commercial, industrial and military applications, and is comprised of departments that design, manufacture, operate and maintain the aircraft or spacecraft. Among the first advocates of 3D printing, the airline industry is a driving force in the evolution of this technology for both manufacturing end-use parts and prototyping. Airlines depend on 3D printing to alleviate supply chain constraints, limit warehouse space and reduce wasted materials from traditional manufacturing processes. Rapidly producing aircraft parts on demand saves enormous amounts of space, time and money.

3D printing technology was appealing proposition for the automotive industry at an early stage and additive manufacturing is increasing used in the sector. The 2015 Wohlers report states that the motor vehicles constituted 16.1% of the 3D printing market that year. The recent advances in additive manufacturing, allowing for newer designs, reduced lead times, and decreased costs, are already paving the way for novel ways of conceiving and producing motor vehicles.
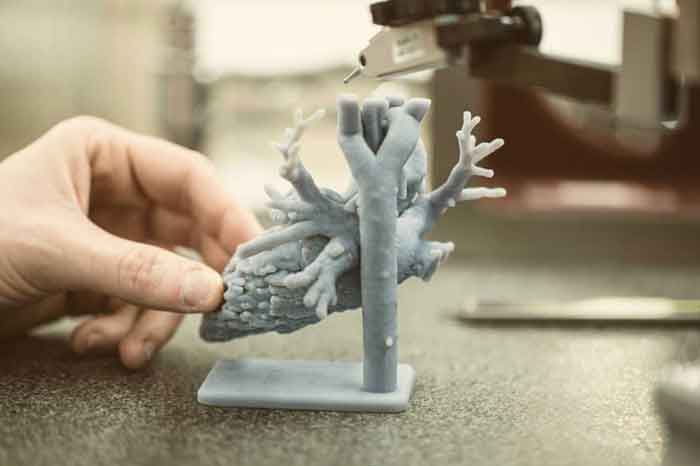

Medical applications for 3D printing are expanding rapidly and are expected to revolutionize health care. Medical uses for 3D printing, both actual and potential, can be organized into several broad categories, including: tissue and organ fabrication; creation of customized prosthetics, implants, and anatomical models; and pharmaceutical research regarding drug dosage forms, delivery, and discovery. The application of 3D printing in medicine can provide many benefits, including: the customization and personalization of medical products, drugs, and equipment; cost-effectiveness; increased productivity; the democratization of design and manufacturing; and enhanced collaboration.
3D printing is proving to be one of the most game-changing technologies of recent times,
giving consumers the ability to produce real-life, 3D objects in their own homes.
With developers and the general public introducing more and more applications of the
technology,
interest is certainly picking up.
3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing, which should give a major hint to how the
process works. In a nutshell,
the objects 3D printers produce are created by adding many different layers until the
intended object is formed.

3D printing is any of various processes in which material is joined or solidified under computer control to create a three-dimensional object,with material being added together (such as liquid molecules or powder grains being fused together), typically layer by layer. In the '90s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only to the production of functional or aesthetical prototypes and, back then, a more comprehensive term for 3D printing was rapid prototyping.
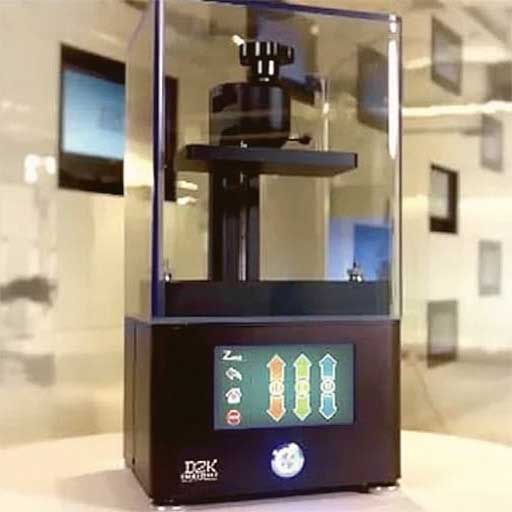
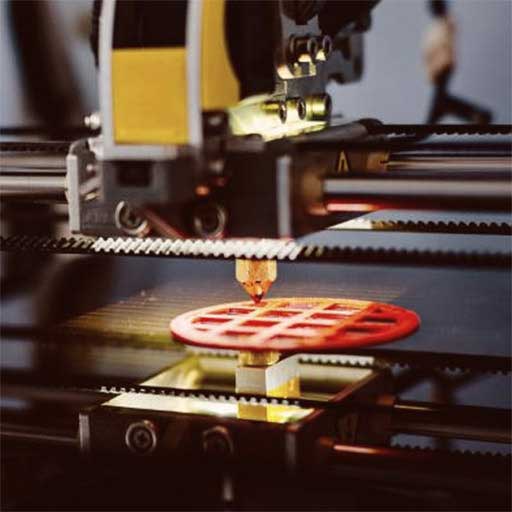
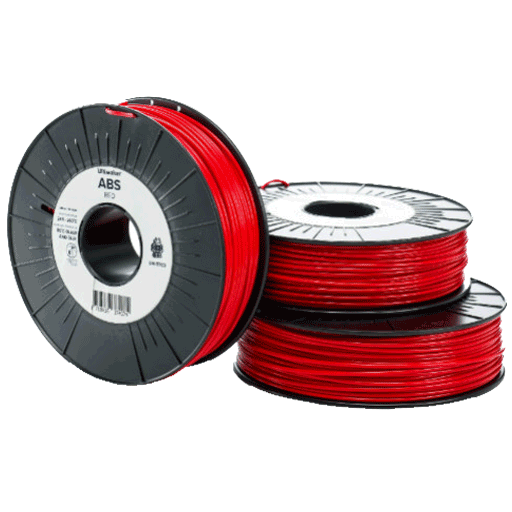
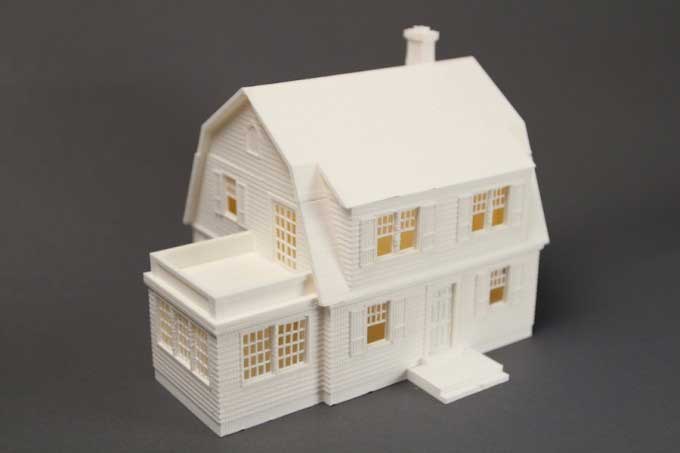
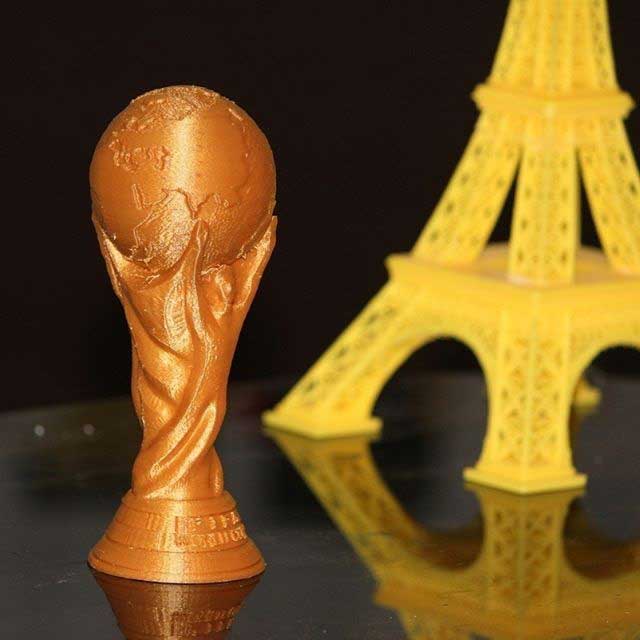
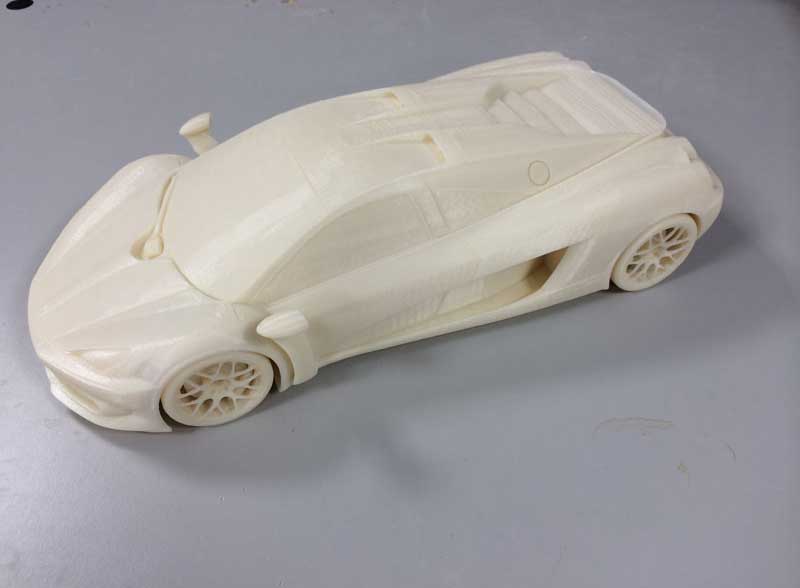
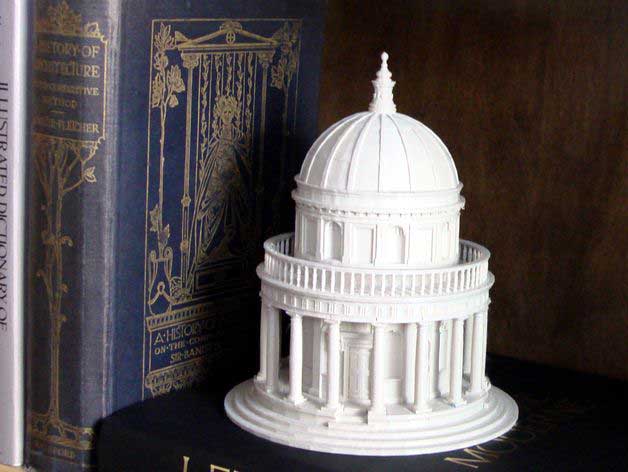
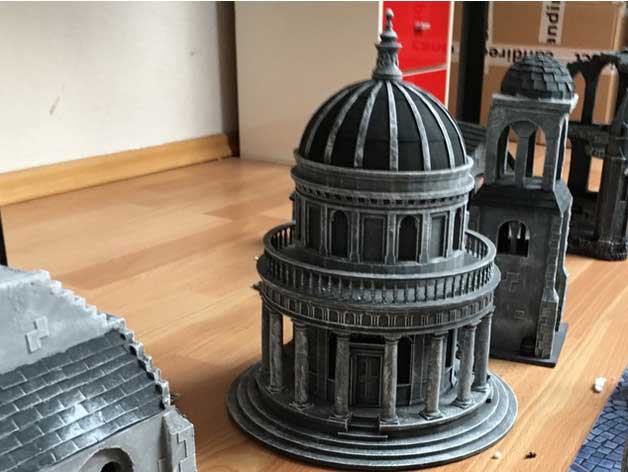
























3D Printing is a means to visualize your 2D Designs in the real world made out of Tough, Durable and Bio-Degradable modified Plastic like PLA, ABS, PETG. Make your vision a reality by 3d-printing any design conceivable. If you can design it, we can print it.
| DIMENSION (mm) | WEIGHT |
|---|---|
| MATERIAL | |
|---|---|
| QUANTITY |
* Send Enquiry for bulk orders